
I know this is a lot to take in, but there are several videos and articles on Khan Academy to help. DNA is a complete set of instructions needed for life (unless you're a virus, but that's a whole different story/debate) and RNA is used to copy DNA and to synthesize proteins. RNA is single-stranded and is generally straight. Uracil links to adenine in RNA just like thymine does in DNAįinally, DNA is double-stranded and forms a double helix structure. Thymine had the chemical formula C5H6N2O2 and uracil is C4H4N2O2. The important features of the TOPO Tools Elements. Instead, it has uracil, a nucleiotide base with a slightly different chemical makeup. The resulting linear DNA construct is used to generate RNA transcripts or protein from your PCR product. You probably know that DNA has guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine, and that guanine links to cytosine and adenine links to thymine. Second, while each has four nucleiotide bases, there is one difference. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. It’s a cyclical moleculemost of its atoms are arranged in a ring-structure. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose.

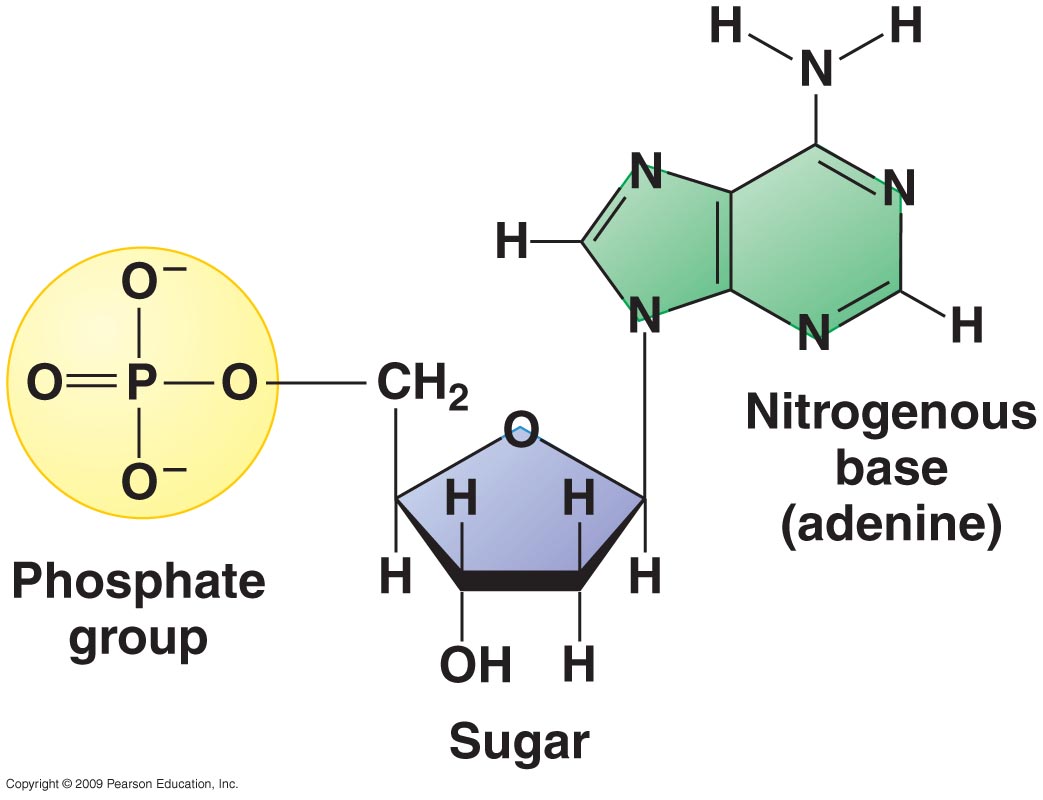
The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The sugar and acid in all four monomers are the same All four nucleotides (A, T, G and C) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. 1 They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. These names describe the sugar that makes up their backbone-DNA = deoxyribose and RNA = ribose. Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. To start, DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, while RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. Since then, researchers have used a variety of in vitro and in vivo assays to demonstrate that proteins interact with DNA and RNA to influence the structure and function of the.
In the late 19th century, scientists microscopically observed the association of proteins with DNA strands. In Nucleic Acids Research, researchers present a method known as RNAcanvas to automate and improve two-dimensional nucleic acid structure drawings. Ministry of Education Key Laboratory for Membraneless Organelles and Cellular Dynamics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China.If you are asking what the difference between the two is, here you go. Overview of ProteinNucleic Acid Interactions. 20 hours ago &0183 &32 In Nucleic Acids Research, researchers present a method known as RNAcanvas to automate and improve two-dimensional nucleic acid structure drawings. Collectively, our studies demonstrate that ZBTB7A mainly employs its ZF1-2 to recognize the PNT-associated sequence but recognizes γ-globin -200 gene element via ZF1-4, providing insights into the molecular mechanism for the diversity of ZBTB7A's genomic localization. The mutations of key residues in ZF1-2 remarkably reduce their binding affinities for the PNT-associated sequence in vitro and cannot restore epiblast stem cells to the naïve pluripotent state in vivo.

The structure shows that ZF1 and ZF2 primarily contribute to recognizing the GACCC core sequence mimicking the half part (GCCCC) of γ-globin -200 gene element via specific hydrogen bonding and van der Waals contacts. Here, we report a crystal structure of ZBTB7A ZF1-3 in complex with the PNT-associated sequence. Recently, it has been reported that ZBTB7A drives primed-to-naïve transition (PNT) of pluripotent stem cells through binding to a 12-bp consensus sequence (, referred to as PNT-associated sequence). Our previously determined crystal structure of ZBTB7A in complex with a GCCCCTTCCCC sequence revealed that all four ZFs (ZF1-4) are involved in binding to γ-globin -200 gene element to repress fetal haemoglobin expression. ZBTB7A, a transcription factor containing a tandem array of four Cys2-His2 zinc fingers (ZFs), is vital for multiple physiological events through directional binding to different genomic loci. Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Access.Citation, Usage, Privacy Policies, Logo.Biologically Interesting Molecule Reference Dictionary (BIRD).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
